Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
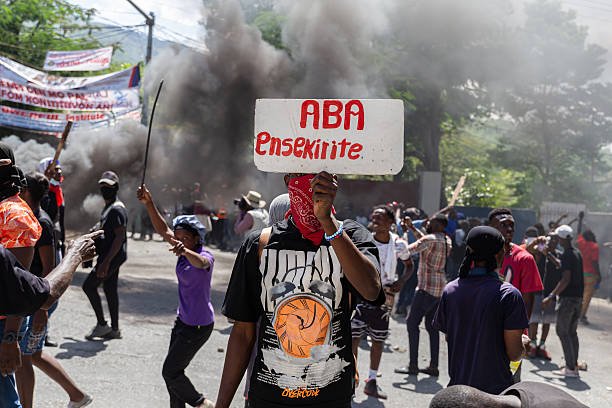
The 4 Sadistic Alliance of Haiti Destruction: Politicians, Oligarchs, Foreign Actors, and Gangs.
Haiti’s ongoing instability is a result of a complex interplay of forces. A destructive alliance has formed, comprising various groups that contribute to the chaos.
Politicians and oligarchs have played significant roles in exacerbating the situation, often prioritizing personal gain over the welfare of the Haitian people.
The influence of foreign actors and the rise of powerful gangs have further complicated the landscape, creating a volatile environment that hinders efforts towards peace and stability.
Haiti, the first independent black nation in the world, has a history deeply intertwined with the legacy of colonial rule and the struggle against it. This historical context is crucial for understanding the complexities of Haiti’s current situation.
Haiti was a French colony, known as Saint-Domingue, which was one of the most profitable colonies in the world due to its vast plantations worked by enslaved Africans. The brutal conditions and the influence of the French Revolution led to a successful slave revolt in 1791, led by figures like Toussaint Louverture. This revolution culminated in Haiti’s independence in 1804, making it the first country in the world to be established as a result of a successful slave revolt.
Despite achieving independence, Haiti faced numerous challenges, including a hefty indemnity imposed by France, which drained its resources, and political instability marked by coups and power struggles. The country’s early promise was hindered by external pressures and internal conflicts, setting a pattern of instability that continued for centuries.
Today, Haiti’s historical legacy of exploitation and instability has contributed to its vulnerabilities. The country struggles with political corruption, economic underdevelopment, and social inequality. These factors have made Haiti one of the poorest countries in the Western Hemisphere, with a significant portion of its population living below the poverty line.
The cycle of exploitation and instability continues to affect Haiti, with foreign interventions, political mismanagement, and gang violence exacerbating the situation. Understanding this historical context is essential for grasping the complexities of Haiti’s current challenges and the sadistic alliance that perpetuates its suffering.
A closer look at Haiti reveals a destructive alliance between politicians, oligarchs, foreign actors, and gangs that contributes to the country’s ongoing instability. This complex web of relationships has been a significant factor in Haiti’s persistent turmoil.
The term “destructive alliance” refers to the collaboration between different powerful entities that work together to maintain their power and control over Haiti, often at the expense of the general population. This alliance is characterized by a mutual interest in exploiting Haiti’s resources and maintaining the status quo of instability.
The interaction between politicians, oligarchs, foreign actors, and gangs in Haiti is multifaceted. Politicians often rely on oligarchs for financial support, while oligarchs use their economic influence to shape political decisions. Foreign actors provide aid and investment, but sometimes their interests align with those of the oligarchs, perpetuating exploitation. Gangs, often backed by political figures, enforce control through violence.
The destructive alliance perpetuates a cycle of exploitation and instability. As politicians and oligarchs exploit Haiti’s resources, they maintain a system that keeps the population in poverty. Gangs, backed by political figures, contribute to the instability, making it difficult for the country to develop.
| Entity | Role in Destructive Alliance | Impact on Haiti |
|---|---|---|
| Politicians | Provide governance, often corrupt | Maintain power, exploit resources |
| Oligarchs | Control the economy, influence politics | Exploit resources, widen wealth gap |
| Foreign Actors | Provide aid, investment | Can perpetuate dependency, align with oligarchs |
| Gangs | Enforce control through violence | Contribute to instability, fear among the population |
Understanding this destructive alliance is crucial to addressing Haiti’s problems. By recognizing how these forces interact and perpetuate instability, it’s possible to begin working towards a more equitable and stable future for Haiti.
Governance in Haiti has become synonymous with personal enrichment, as politicians navigate a complex web of corruption and patronage. This phenomenon is not new but has been a persistent issue throughout Haiti’s history.
Political corruption in Haiti is deeply ingrained, with politicians often using their positions to amass wealth. This is achieved through various means, including embezzlement, bribery, and cronyism. The lack of transparency and accountability in government operations facilitates this corruption, making it difficult to track and prosecute.
Several key political figures have played significant roles in shaping Haiti’s political landscape. Their actions, or lack thereof, have contributed to the current state of corruption and instability. For instance, leaders have been known to prioritize their personal interests over the needs of the population, exacerbating poverty and inequality.
Failed governance in Haiti has led to severe consequences, including economic stagnation, increased poverty, and heightened insecurity. The inability of political leaders to effectively govern has created a power vacuum, which is often filled by other actors, including gangs and foreign entities.
The administration of President Jovenel Moïse is a recent example of how political power has been exploited for personal gain. During his tenure, Moïse faced numerous allegations of corruption and authoritarianism, which ultimately contributed to his assassination in 2021. His administration’s failure to address the country’s pressing issues, such as gang violence and economic instability, further underscored the governance challenges in Haiti.
The Moïse administration’s legacy highlights the entrenched nature of corruption and the challenges faced in efforts to reform the political system. It also underscores the need for greater accountability and transparency in Haitian politics.
The concentration of economic power in the hands of Haiti’s oligarchic elite has led to pronounced social divisions. This elite group has maintained control over the economy, influencing key sectors and shaping the country’s social landscape.
Haiti’s economy is characterized by a significant concentration of wealth among a few powerful families. These oligarchs control key industries such as agriculture, finance, and trade, thereby exerting considerable influence over the country’s economic policies.
The oligarchic elite’s grip on Haiti’s economy is evident in their dominance of major economic sectors. For instance, a small group of families controls a large portion of the agricultural land, dictating production and pricing.
The oligarchs maintain their control through a combination of economic, political, and social strategies. They often form alliances with political leaders and other influential figures to secure their interests.
The significant wealth gap in Haiti is a direct consequence of the oligarchic elite’s control over the economy. The majority of the population lives in poverty, while a small elite enjoys immense wealth.
The “Five Families” are a prime example of Haiti’s oligarchic elite. They have historically controlled large swaths of the economy and have maintained their power through strategic alliances and economic dominance.
| Family | Primary Economic Interests | Political Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Family 1 | Agriculture, Finance | High |
| Family 2 | Trade, Manufacturing | Moderate |
| Family 3 | Finance, Real Estate | High |
| Family 4 | Agriculture, Energy | Moderate |
| Family 5 | Trade, Construction | High |
The influence of the “Five Families” is a critical factor in understanding Haiti’s economic and social dynamics. Their control over key sectors and their political influence perpetuate the cycle of poverty and inequality.
The role of foreign actors in Haiti is multifaceted, involving historical interventions, ongoing aid, and geopolitical interests. This complex dynamic has significantly impacted Haiti’s development and stability.
Haiti has experienced numerous foreign interventions throughout its history. The most notable include the U.S. occupation from 1915 to 1934 and the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH) from 2004 to 2017. These interventions have had lasting impacts on Haiti’s political and social structures.
For instance, the U.S. occupation led to the centralization of power and the creation of a modern military, but it also suppressed Haitian culture and reinforced dependency on foreign powers. Similarly, MINUSTAH was mandated to stabilize Haiti after the 2004 coup, but it faced criticism for its handling of the cholera outbreak it inadvertently introduced, which killed thousands of Haitians.
International aid has been a crucial component of Haiti’s economy, but it also poses significant challenges. While aid provides essential resources for survival and development, it can create dependency and undermine local capacities. Moreover, aid is often tied to conditions that benefit donor countries more than Haiti.
Aid can be categorized into humanitarian assistance, development aid, and military aid. Humanitarian aid is critical during crises, but it is meant to be temporary. Development aid aims to support long-term projects, yet it is often marred by inefficiencies and corruption. Military aid, on the other hand, can perpetuate a cycle of violence and dependency on foreign military presence.
| Type of Aid | Purpose | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Humanitarian Aid | Emergency relief | Temporary can create dependency |
| Development Aid | Long-term projects | Inefficiencies, corruption |
| Military Aid | Security support | Perpetuates violence, dependency |
Geopolitical interests play a significant role in shaping foreign interventions and aid in Haiti. Major powers like the United States and France have historical and strategic interests in the region.
The United States has been a dominant player in Haitian affairs, driven by its geopolitical and economic interests. France, Haiti’s former colonial ruler, continues to exert influence, particularly in the economic sphere. Other nations, including Canada and Brazil, have also contributed to MINUSTAH and provided aid, reflecting their own geopolitical interests.
These foreign actors often pursue their interests under the guise of humanitarian or development aid, which can lead to a form of neocolonialism. Understanding these dynamics is crucial to grasping the full picture of Haiti’s challenges and the role of foreign actors within them.
Haiti’s struggle with gang violence is a complex issue, deeply intertwined with the country’s political and social fabric. The presence of gangs has become a pervasive element in the daily lives of Haitians, influencing security, economic stability, and social cohesion.
The rise of gangs in Haiti can be attributed to various factors, including historical instability, economic hardship, and a lack of effective governance. Over the years, gangs have filled the power vacuum created by weak state institutions, gradually expanding their territorial control and influence.
Gangs have become adept at exploiting local grievances, often presenting themselves as protectors of their communities. However, their actions are frequently marked by violence and intimidation, contributing to a climate of fear.
Gangs in Haiti are not isolated entities; they have significant connections to political figures and parties. These relationships are often characterized by patronage and mutual benefit, where gangs receive support or protection in exchange for delivering votes, maintaining order, or suppressing opposition.
The impact of gang violence on daily life in Haiti is profound. Citizens live in constant fear of attacks, kidnappings, and extortion. Businesses are often forced to pay “taxes” to gangs, adding to the economic burden on the population. The presence of gangs also hampers access to basic services, as areas controlled by gangs can be off-limits to government officials and aid workers.
Some gang leaders have gained notoriety for their control over significant territories and their influence on local politics. The following table highlights a few prominent gang leaders and their areas of operation:
| Gang Leader | Area of Control | Notable Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Jimmy “Barbecue” Chérizier | Port-au-Prince and surrounding areas | Alleged involvement in multiple violent incidents, including massacres and kidnappings. |
| Joseph “Lanmo” Pierre | Parts of Port-au-Prince | Known for controlling key intersections and demanding ransoms. |
| René “Ti Renè” Saint-Fort | Various neighbourhoods in Port-au-Prince | Accused of extortion and violent turf wars with rival gangs. |

The activities of these gang leaders underscore the complexity of gang dynamics in Haiti and the challenges faced by authorities in addressing gang violence.
At the heart of Haiti’s turmoil lies a sophisticated network of alliances between political figures, oligarchs, foreign influencers, and gang leaders. This complex web of relationships is crucial in understanding how the “4 Sadistic Alliance” maintains its grip on the country.
The relationship between Haitian politicians and oligarchs is deeply intertwined. Politicians often rely on oligarchs for financial backing during elections, and in return, they may offer favourable policies or protection from prosecution. This symbiotic relationship allows both parties to benefit at the expense of the general population.
Foreign actors, including governments and international organizations, play a significant role in Haiti’s domestic politics. They provide financial aid, which can be used to influence policy decisions or support specific political candidates. This external influence can undermine the sovereignty of Haiti and perpetuate the cycle of dependency.
Gangs have become increasingly powerful in Haiti, often serving as tools of control for political and oligarchic interests. They are used to intimidate opponents, influence election outcomes, and maintain social order through violence. The connection between gangs and powerful figures is a critical aspect of the alliance’s functionality.
Several instances illustrate the collaboration between these groups. For example, during election periods, gangs have been known to be hired by political candidates to secure votes or intimidate opponents. Similarly, oligarchs have been linked to gang activities, providing them with financial and logistical support.
The circulation of resources within the alliance is a key factor in its persistence. Money, weapons, and influence are distributed among the members of the alliance, ensuring that each component remains loyal and effective. The following table illustrates the flow of resources within the alliance:
| Resource | Source | Destination | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Money | Oligarchs, Foreign Aid | Politicians, Gangs | Funding campaigns, buying loyalty |
| Weapons | Foreign Suppliers | Gangs | Maintaining control, intimidating opponents |
| Power | Politicians, Oligarchs | Influence over policy and law enforcement | Protecting interests, avoiding accountability |
The intricate web of relationships within the “4 Sadistic Alliance” is a major obstacle to Haiti’s development and stability. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing effective strategies to break the cycle of violence and corruption.
Haiti’s population is bearing the brunt of a complex crisis fueled by a destructive alliance of politicians, oligarchs, foreign actors, and gangs. The consequences of this alliance are far-reaching, impacting every aspect of life for Haitians.
The economic situation in Haiti is dire, with widespread poverty and a lack of access to necessities like food, clean water, and healthcare. The economic devastation is a direct result of the corrupt practices of the ruling elite and the exploitation by foreign actors.
Many Haitians struggle to make ends meet, living in precarious conditions that are exacerbated by the lack of economic opportunities and infrastructure.
Security is a major concern in Haiti, with gang violence becoming increasingly prevalent. Gangs often act with impunity, perpetrating violence and intimidation that affects daily life for ordinary Haitians.
The presence of gangs has led to a culture of fear, with many people unable to leave their homes or go about their daily lives without risking violence or harassment.
The crisis in Haiti has also led to a significant refugee crisis, with many Haitians fleeing their homeland in search of safety and better opportunities. The diaspora community plays a crucial role in supporting those left behind, but the loss of talent and skills further weakens the country.
Stories from Haitians on the ground paint a vivid picture of the human cost of the crisis. For example, a mother in Port-au-Prince might describe the constant fear of gang violence and the struggle to provide for her children.
These personal narratives highlight the urgent need for change and the importance of addressing the root causes of the crisis.

Haiti’s complex web of destruction, woven by the intertwined interests of politicians, oligarchs, foreign actors, and gangs, demands a multifaceted solution. To break the cycle of instability and pave the way for a brighter Haiti’s future, it’s crucial to address the systemic issues that enable this destructive alliance.
Reform efforts should focus on enhancing transparency and accountability within the government, reducing the oligarchs’ stranglehold on the economy, and reevaluating the role of foreign aid to ensure it benefits the local population rather than perpetuating dependency. Change can be achieved by supporting local initiatives and empowering communities to drive their development.
Ultimately, breaking the cycle of destruction requires a concerted effort from both within Haiti and from the international community. By working together to implement meaningful reform and support sustainable development, Haiti can begin to heal and move towards a more stable and prosperous future.
The “4 Sadistic Alliance” refers to the complex interplay of forces contributing to Haiti’s instability, involving politicians, oligarchs, foreign actors, and gangs.
Haiti’s colonial past, journey towards independence, and subsequent challenges have all contributed to its current state of instability, making it vulnerable to exploitation by various forces.
Haitian politicians have been known to exploit their power for personal gain, perpetuating corruption and failed governance, which contributes to the country’s instability.
The oligarchic elite maintains control through their economic power structure, perpetuating social divisions and a significant wealth gap, which has severe implications for the country.
Foreign interventions and international aid have had a double-edged effect on Haiti, sometimes providing necessary support, but also perpetuating dependency and exploitation.
Gangs have risen to prominence through their connections to political figures and patronage, becoming a significant force in the country’s instability and daily violence.
The “4 Sadistic Alliance” has led to economic devastation, security concerns, daily violence, and a refugee crisis, severely impacting the lives of Haitians and their future.
The forces within the alliance interact through complex relationships, including political-oligarchic connections, foreign influence on domestic politics, and the use of gangs as tools of control.
Breaking the cycle of destruction will require comprehensive solutions, including reform and positive change, to address the complex issues perpetuated by the “4 Sadistic Alliance.”